eCommerce sales are expected to grow at an average rate of 6.29% each year between 2025 and 2030.
As more shoppers rely on online stores, many entrepreneurs are exploring how to launch their own eCommerce businesses.
The guide below outlines 10 key steps to help you get started, provides practical tips to improve conversions, and offers an overview of the costs you’re likely to encounter along the way.
10 Simple Steps To Start An Ecommerce Business In 2026
In this guide, we’ll walk through 10 essential steps to help you start your ecommerce business. Whether you’re a first-time founder or an experienced entrepreneur, these practical steps will help you build a profitable online business.
Step 1: Decide What to Sell
More than 2.7 billion people shop online worldwide, creating a large audience you can reach with the right products.
Whether you’re selling your own products or sourcing items from suppliers, choosing what to sell is the foundation of your ecommerce business.
Understanding different ecommerce business models helps you pick an approach that fits market demand. Common models include:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): Selling directly to customers, like online retailers or fashion brands.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Supplying products or services to other businesses, often in bulk.
- Customer-to-Customer (C2C): Individuals selling to other individuals through platforms like eBay or Facebook Marketplace.
- Customer-to-Business (C2B): Individuals offering services or products to businesses, such as freelancers or influencers.
- Subscription-Based: Offering recurring products or services, such as subscription boxes or digital platforms.
- Dropshipping: Selling products without holding inventory, where a third-party supplier stores and ships ready-made products directly to the customer after a sale.
- Marketplace: Hosting multiple sellers on one platform, like Etsy or Alibaba.
- Wholesale: Selling products in bulk at discounted prices to resellers.
- On-Demand: Selling products without holding inventory, where custom products are produced only after an order is placed, using print-on-demand providers like Printful and Printify.
Choose products that match market demand and your personal interests. For example, personalized products like custom pajamas appeal to niche audiences looking for comfort-focused, giftable items rather than generic apparel.
Look for customer problems you can solve and niches with long-term potential. Take your time, product selection plays a major role in your success.
Step 2: Do Market Research
About 8 out of 10 online shoppers research products before buying, showing how important audience insight and research are for choosing winning products.
Once you have a basic idea of what you want to sell, the next step is market research. This helps you understand your audience, their needs, and how much they’re willing to spend.
Strong research leads to better decisions and improves your chances of success. Start by defining your target audience, including where they live, what they’re interested in, and how they shop online.
Online surveys and social media polls can give direct insight into what potential customers are looking for. You should also explore forums and online communities where your audience spends time, as these spaces often reveal honest opinions, pain points, and preferences.
Studying competitors is equally important. Look at businesses selling similar products and review their pricing, marketing approach, customer reviews, and overall positioning. This research can help you spot gaps in the market and find ways to stand out.
You can also track trends and buying behavior using tools like Statista, Google Trends, and social media analytics. These platforms offer up-to-date data on popular and fast-selling products across ecommerce markets.
For instance, Google Trends may show seasonal spikes for certain products, while social media comments can indicate emerging preferences or style shifts. If your research shows consistent interest in personalized apparel, products such as custom-embroidered clothing may indicate a niche where buyers value quality and customization over mass-produced options.
Combining customer feedback, competitor analysis, and trend data helps you validate ideas before investing, making your product choices more aligned with what people are actively looking to buy.
Step 3: Establish Supply and Inventory
Next, decide how you will source your products. Common options include manufacturers, wholesalers, or dropshipping suppliers.
Cart abandonment rates remain high, near 70%, often due to unexpected costs or slow delivery, which makes supplier reliability and pricing strategy important.
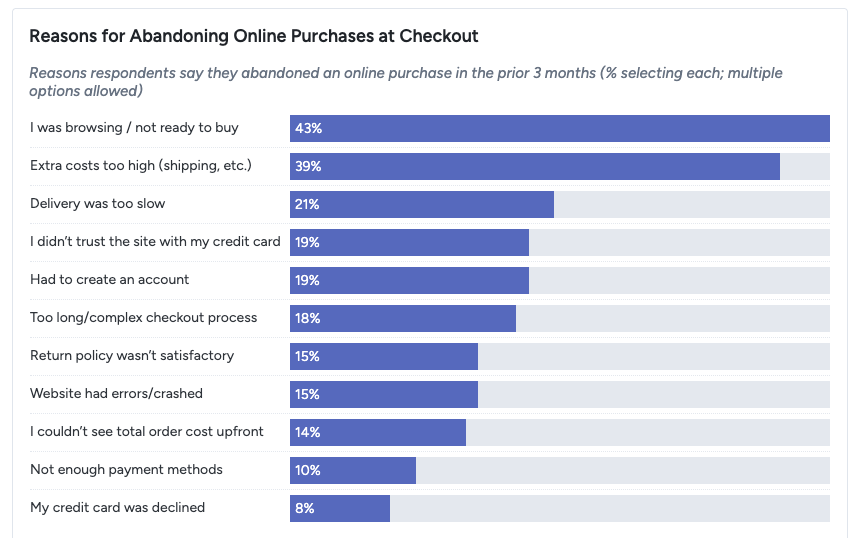
When choosing suppliers, consider product quality, pricing, shipping costs, and reliability. Building strong supplier relationships can lead to smoother operations and better long-term outcomes.
Plan how you will manage inventory by tracking available products and preparing for restocking. A solid inventory system helps prevent both stock shortages and excess inventory by syncing with your ecommerce platform.
Storage is another key consideration. Depending on your business model, you may need warehouse space or third-party fulfillment services to handle storage and shipping. Each option affects costs and logistics, so choose the option that best fits your business.
A well-structured supply and inventory setup helps ensure timely order fulfillment and a better customer experience.
Step 4: Write Your Business Plan
Once you’ve chosen your product, researched the market, and selected suppliers, it’s time to write your business plan.
A business plan outlines your goals and how you plan to reach them. Start with an executive summary that clearly explains your idea. Then describe your product, target audience, and marketing approach.
Include a SWOT analysis to evaluate your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This may involve factors like unique product features, limited experience, market trends, or growing competition.
Finish with financial projections so you understand expected expenses, pricing, and income.
If you’re unsure where to start, free templates are widely available online. Resources from organizations like the Small Business Administration can help guide you through the process.
While writing a business plan takes time, it provides structure and clarity as you prepare to launch.
Step 5: Create Your Brand Identity
Beyond choosing products, building a clear brand identity is an important part of starting your ecommerce business. Your brand helps customers recognize you and builds familiarity over time.
Begin by choosing a business name that is memorable and easy to recall. Once the name is finalized, design a logo that reflects your brand’s personality. Simple, clean designs often work best.
You can use online design tools to experiment with colors and styles or work with a professional designer if needed. Try visualizing how your logo and name will appear on your website, social media, and marketing materials.
A strong brand identity helps you connect with your audience and makes your business easier to remember, so it’s worth investing time to get it right.
Step 6: Build an Ecommerce Store
Now it’s time to create your online store. Before getting started, it’s important to understand the basics of SEO..
SEO helps your website appear in search results, making it easier for potential customers to find you. Learning the fundamentals early will help you structure your site to support long-term visibility.
There are many reliable platforms available for hosting an ecommerce store. These platforms are designed to support secure transactions and often include ready-made templates, built-in payment systems, and simple drag-and-drop builders.
Step 7: Create a Marketing Strategy
Consistent branding and marketing play a major role in driving growth. Studies show that brands that maintain consistency across channels are more likely to generate leads and increase revenue.
Develop a clear ecommerce marketing plan that attracts visitors, builds brand awareness, and encourages repeat purchases.
Your strategy can include digital approaches such as paid advertising and social media campaigns, as well as offline methods like promotional materials or local advertising. No matter which channels you choose, consistency in messaging and branding is key.
A well-planned marketing strategy helps you connect with the right audience and supports steady business growth.
Step 8: Launch Your Ecommerce Store
Once your products and brand are ready, you can move on to launching your store. Following a checklist can help ensure everything works as expected before going live.
One important decision is whether to sell only through your own website or also use online marketplaces. Running your own site gives you full control over design, product presentation, and customer experience, without placing your products next to direct competitors.
If you sell exclusively through your website, you’ll need to actively drive traffic through marketing efforts, as most shoppers won’t discover your store by typing in the URL directly.
Marketplaces, on the other hand, already attract large audiences. Platforms like Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Walmart, Alibaba, and Facebook offer built-in traffic but come with higher competition and pricing pressure.
After launch, track your performance and continue testing different marketing methods to bring more visitors to your store and grow your customer base.
Step 9: Monitor Your Performance
Once your store is live, ongoing monitoring is essential. Ecommerce platforms allow you to test and adjust quickly as you learn what works best.
You can run A/B tests on product descriptions, pricing, or ads to compare results and refine your approach. This helps improve sales decisions without unnecessary risk.
Pay close attention to key metrics such as website traffic, bounce rate, and conversion rate. These indicators reveal how visitors interact with your store and where improvements may be needed.
Mobile performance is especially important, as a large share of online shopping happens on smartphones. Reviewing email engagement can also help you understand how customers respond to updates and promotions.
Regular analysis and small adjustments help strengthen customer relationships and keep your business moving forward.
Step 10: Prioritize Customer Success
Customer experience can make or break an ecommerce business. Many customers will switch to a competitor after just one poor experience.
Providing strong customer support encourages repeat purchases and long-term loyalty.
Strong customer support depends on how well your support team is trained and prepared to handle customer issues. Every support agent plays a direct role in shaping the customer experience through their responses, tone, and problem-solving approach.
To maintain consistency and service quality, new support hires need clear guidance from the start. Using structured employee training templates helps standardize support workflows, outline response guidelines, and ensure every team member follows the same processes when assisting customers, leading to faster resolutions and more reliable support experiences.
You can support customers by offering multiple communication options, such as email, social media, and phone support. Personalizing interactions through tailored FAQs or clear contact options also helps customers find answers faster.
Adding self-service tools, such as help sections or chatbots, enables customers to resolve issues independently when needed. what
By placing customer needs at the center of your operations, you create positive experiences that support retention and sustainable growth.
Summary
In this guide, we covered ten key steps for starting an ecommerce business, from choosing the right products to building a clear and recognizable brand.
Selecting the right business model, carefully planning your marketing, and offering strong customer support are critical to attracting and retaining the right audience.
FAQs
1. Do I need prior business experience to start an ecommerce business in 2026?
No. Many successful ecommerce businesses are started by first-time founders. What matters more is choosing the right product, understanding your audience, and learning as you go. With user-friendly ecommerce platforms and widely available learning resources, beginners can start small and build confidence over time.
2. How much money do I need to start an ecommerce business?
The startup cost depends on your business model. Dropshipping and print-on-demand usually require less upfront investment, while holding inventory or manufacturing products costs more. At a minimum, you should budget for your website, basic branding, marketing, and initial product setup.
3. Should I sell on my own website or use online marketplaces?
Both options have pros and cons. Selling through your own website gives you full control over branding and customer experience, but you need to bring in traffic yourself. Marketplaces already have shoppers, but competition is higher and fees can reduce margins. Many businesses start with one and add the other later.
4. How long does it take to see results from an ecommerce store?
Results vary. Some stores make their first sale within weeks, while others take months. Success depends on product demand, pricing, marketing consistency, and customer experience. Regular testing, tracking performance, and small improvements over time usually lead to steady progress.
5. What are the most common mistakes new ecommerce businesses make?
Common mistakes include choosing products without research, underestimating marketing needs, poor inventory planning, and ignoring customer feedback. Skipping a business plan or launching without testing the store can also cause issues. Taking time to plan and review performance helps avoid many early problems.




